“Forbearance did not hit 30%, but rather peaked at 8.6% and has been steadily falling since.”
Originally, some housing industry analysts were concerned that the mortgage forbearance program (which allows families to delay payments to a later date) could lead to an increase in foreclosures when forbearances end. Some even worried that we might relive the 2006-2008 housing crash all over again. Once you examine the data, however, that seems unlikely.
As reported by Odeta Kushi, Deputy Chief Economist for First American:
“Despite the federal foreclosure moratorium, there were fears that up to 30% of homeowners would require forbearance, ultimately leading to a foreclosure tsunami. Forbearance did not hit 30%, but rather peaked at 8.6% and has been steadily falling since.”
According to the most current data from Black Knight, the percentage of homes in forbearance has fallen to 7.4%. The report also gives the decrease in raw numbers:
“The overall trend of incremental improvement in the number of mortgages in active forbearance continues. According to the latest data from Black Knight’s McDash Flash Forbearance Tracker, the number of mortgages in active forbearance fell by another 71,000 over the past week, pushing the total under 4 million for the first time since early May.”
Here’s a graph showing the decline in forbearances over the last several months: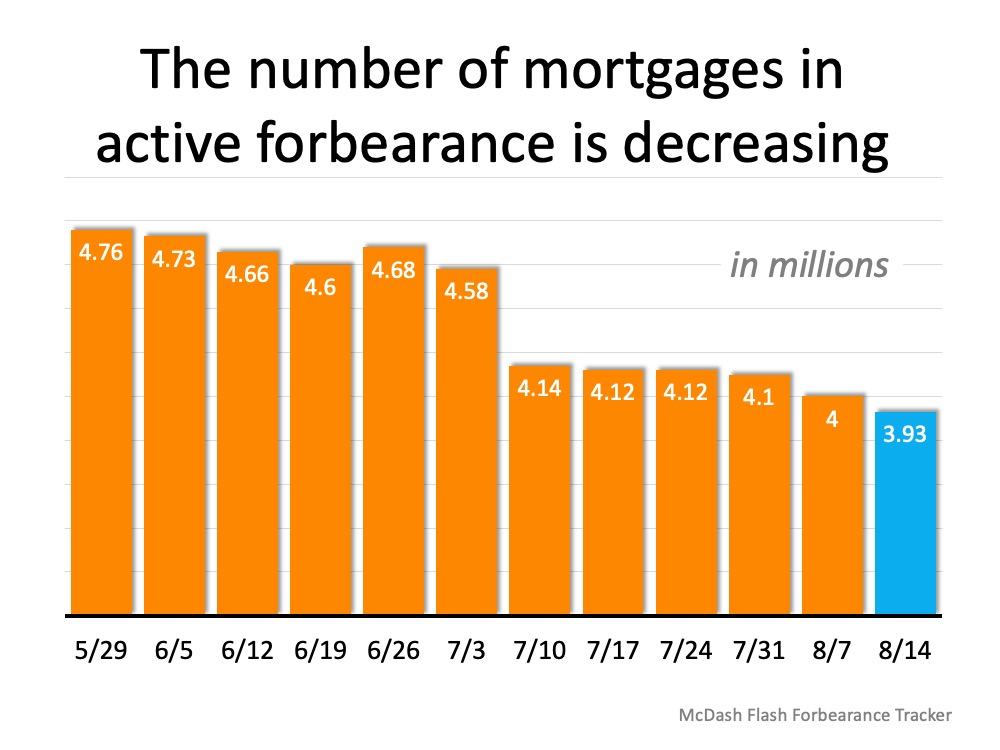 The report also explains that across the board, overall forbearance activity fell with 10% fewer new forbearance requests and nearly 40% fewer renewals.
The report also explains that across the board, overall forbearance activity fell with 10% fewer new forbearance requests and nearly 40% fewer renewals.
What about potential foreclosures once forbearances end?
Kushi also addresses this question:
“There are two main reasons why this crisis is unlikely to produce a wave of foreclosures similar to the 2008 recession. First, the housing market is in a much stronger position compared with a decade ago. Accompanied by more rigorous lending standards, the household debt-to-income ratio is at a four-decade low and household equity near a three-decade high. Indeed, thus far, MBA data indicates that the majority of homeowners who took advantage of forbearance programs are either staying current on their mortgage or paying off the loan through a home sale or a refinance. Second, this service sector-driven recession is disproportionately impacting renters.”
There is one potential challenge
Today, the options available to homeowners will prevent a large spike in foreclosures. That’s good not just for those families impacted, but for the overall housing market. A recent study by Fannie Mae, however, reveals that many Americans are not aware of the options they have.
It’s imperative for potentially impacted families to better understand the mortgage relief programs available to them, for their personal housing situation and for the overall real estate market.
Bottom Line
If Americans fully understand their options and make good choices regarding those options, the current economic slowdown does not need to lead to mass foreclosures.
To view original article, visit Keeping Current Matters.
How Eco-Friendly Features Can Boost Your Home’s Value
Not sure which upgrades to prioritize? That’s where a local real estate agent comes in.
The Biggest Perks of Buying a Home This Winter
Since homes generally take longer to sell during the winter, sellers are often more motivated to close a deal.
How Home Equity May Help You Buy Your Next Home in Cash
Building equity in your house is one of the biggest financial advantages of homeownership.
Struggling To Sell Your House? Read This.
If you’re having trouble getting your house sold, here are the top three hurdles and how an expert agent can help you solve these issues.
Only an Expert Agent Can Give You an Accurate Value of Your Home
Agents have a deep understanding of the local market, and they can provide insights that automated tools simply can’t match.
What Will It Take for Prices To Come Down?
It’s crucial to work with a local real estate expert who understands your market and can explain what’s going on where you live.





