
“Let’s break down why more people are using adjustable-rate mortgages and why this isn’t cause for concern.”
f you remember the housing crash back in 2008, you may recall just how popular adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) were back then. And after years of being virtually nonexistent, more people are once again using ARMs when buying a home. Let’s break down why that’s happening and why this isn’t cause for concern.
Why ARMs Have Gained Popularity More Recently
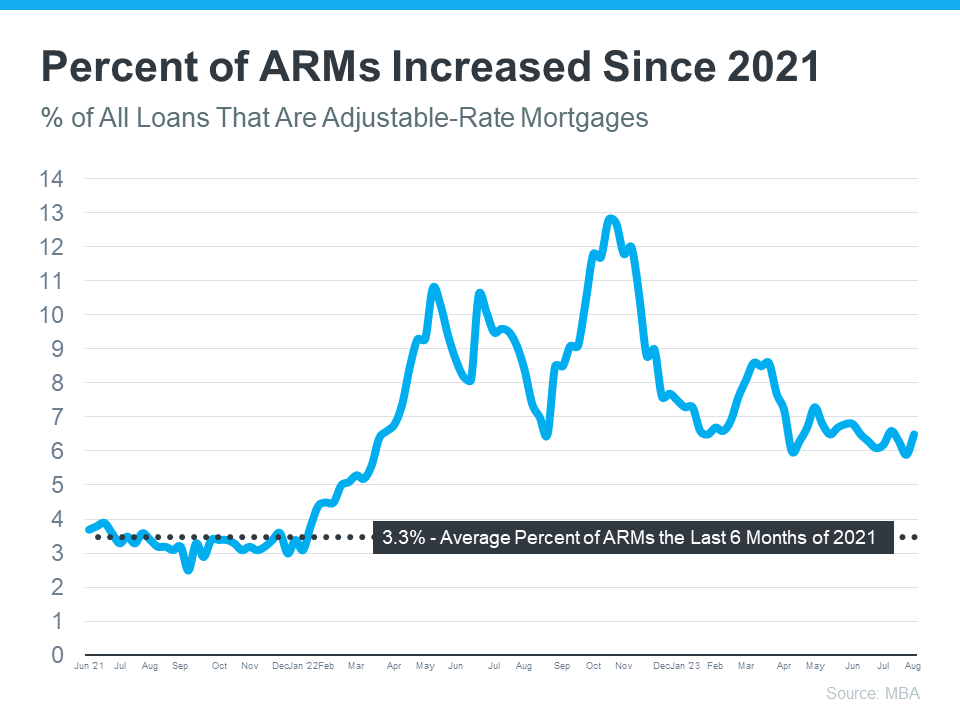
This graph uses data from the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) to show how the percentage of adjustable-rate mortgages has increased over the past few years:
As the graph conveys, after hovering around 3% of all mortgages in 2021, many more homeowners turned to adjustable-rate mortgages again last year. There’s a simple explanation for that increase. Last year is when mortgage rates climbed dramatically. With higher borrowing costs, some homeowners decided to take out this type of loan because traditional borrowing costs were high, and an ARM gave them a lower rate.
Why Today’s ARMs Aren’t Like the Ones in 2008
To put things into perspective, let’s remember these aren’t like the ARMs that became popular leading up to 2008. Part of what caused the housing crash was loose lending standards. Back then, when a buyer got an ARM, banks and lenders didn’t require proof of their employment, assets, income, etc. Basically, people were getting loans that they shouldn’t have been awarded. This set many homeowners up for trouble because they couldn’t pay back the loans that they never had to qualify for in the first place.
This time around, lending standards are different. Banks and lenders learned from the crash, and now they verify income, assets, employment, and more. This means today’s buyers actually have to qualify for their loans and show they’ll be able to repay them.
Archana Pradhan, Economist at CoreLogic, explains the difference between then and now:
“Around 60% of Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM) that were originated in 2007 were low- or no-documentation loans . . . Similarly, in 2005, 29% of ARM borrowers had credit scores below 640 . . . Currently, almost all conventional loans, including both ARMs and Fixed-Rate Mortgages, require full documentation, are amortized, and are made to borrowers with credit scores above 640.”
In simple terms, Laurie Goodman at Urban Institute helps drive this point home by saying:
“Today’s Adjustable-Rate Mortgages are no riskier than other mortgage products and their lower monthly payments could increase access to homeownership for more potential buyers.”
Bottom Line
If you’re worried today’s adjustable-rate mortgages are like the ones from the housing crash, rest assured, things are different this time.
And, if you’re a first-time homebuyer and you’d like to learn more about lending options that could help you overcome today’s affordability challenges, reach out to a trusted lender.
To view original article, visit Keeping Current Matters.
Expert Housing Market Forecasts for the Second Half of the Year
Housing supply is increasing, but there are still more buyers than there are homes for sale, maintaining the upward pressure on home prices.
The Drop in Mortgage Rates Brings Good News for Homebuyers
A decrease in mortgage rates means an increase in your purchasing power.
Is Homeownership Still the American Dream?
Your home is your stake in the community and a strong financial investment, something you can be proud of.
If You’re Selling Your House This Summer, Hiring a Pro Is Critical
Today’s market is at a turning point, making it more essential than ever to work with a real estate professional.
Two Reasons Why Today’s Housing Market Isn’t a Bubble
Today, there’s still a shortage of inventory, which is causing ongoing home price appreciation.
The Average Homeowner Gained $64K in Equity over the Past Year
In addition to building your overall net worth, equity can also help you achieve other goals like buying your next home.







.jpg )



